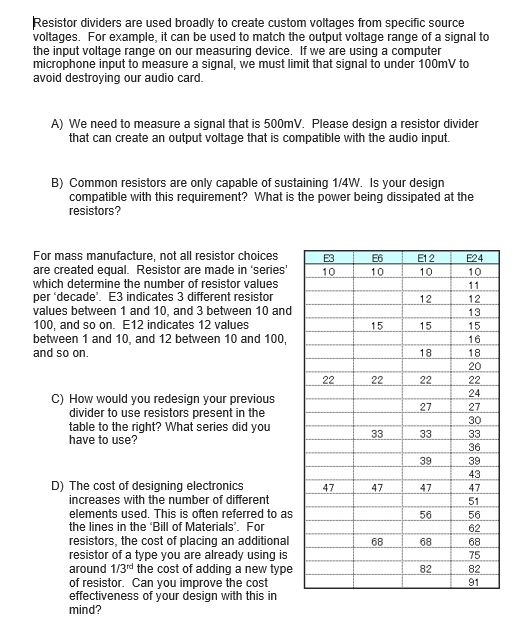
Solved For the voltage divider shown above calculate the Circuit Diagram
BlogSolved For the voltage divider shown above calculate the Circuit Diagram Understanding Voltage Dividers. A voltage divider works on the principle of ohm's law, which states that the voltage across a resistor is proportional to the current flowing through it and the resistance of the resistor.By selecting the appropriate resistor values, a voltage divider can be used to scale down a high voltage to a lower voltage, making it suitable for a wide range of applications. In electronics, a voltage divider (also known as a potential divider) is a passive linear circuit that produces an output voltage (V out) that is a fraction of its input voltage (V in). Voltage division is the result of distributing the input voltage among the components of the divider. A simple example of a voltage divider is two resistors connected in series, with the input voltage applied

A voltage divider is a simple circuit that can reduce voltage. It distributes the input voltage among the components of the circuit. The best example of a voltage divider is two resistors connected in series, with the input voltage applied across the resistor pair and the output voltage taken from a point between them. It is used to produce different voltage levels from a common voltage source Once you understand how a voltage drops over a resistor, you're about halfway done with understanding a voltage divider. If you need a voltage lower in your circuit than the voltage that is provided by your power source, you can use a voltage divider. a potentiometer is a voltage divider that changes the resistance values depending on Key learnings: Voltage Divider Definition: A voltage divider is a simple circuit that creates a part of its input voltage as output, using two resistors in series.; Circuit Components: The circuit includes two resistors connected in series with a voltage source, splitting the input voltage.; Unloaded Equation: With no current flowing out, the output voltage depends on the ratio of the resistors.

Understanding Resistive Voltage Divider Circuits through Calculations Circuit Diagram
One final point about capacitive voltage divider circuits is that as long as there is no series resistance, purely capacitive, the two capacitor voltage drops of 69 and 31 volts will arithmetically be equal to the supply voltage of 100 volts as the two voltages produced by the capacitors are in-phase with each other. If for whatever reason the Understanding Voltage Dividers. A voltage divider is a simple yet powerful circuit that generates a specific voltage output from a higher input voltage. It is achieved using two resistors connected in series across a voltage supply. Vin is the input voltage. R1 is the resistance of the first resistor. R2 is the resistance of the second For a voltage divider, understanding how the voltage gets divided across the resistors is directly linked to Ohm's law. Let's consider the current flowing through the circuit. Since the resistors are in series, the same straight resistive track. The output voltage is adjusted by sliding the wiper, typically controlled by